Nowadays, every factory and manufacturing plant utilized megawatts of energy to run their business. Energy in form of electricity or heat are very critical to operate machines and control processes temperature. Therefore, modern manufacturing facility usually equipped with energy recovery system or waste heat recovery system to optimize the usage of energy.
Typically, heat energy could be generated by combustion of fossil fuel (petroleum, diesel, natural gas, etc.) and biomass inside boiler that produce superheated steam or hot thermal oil as heating medium.
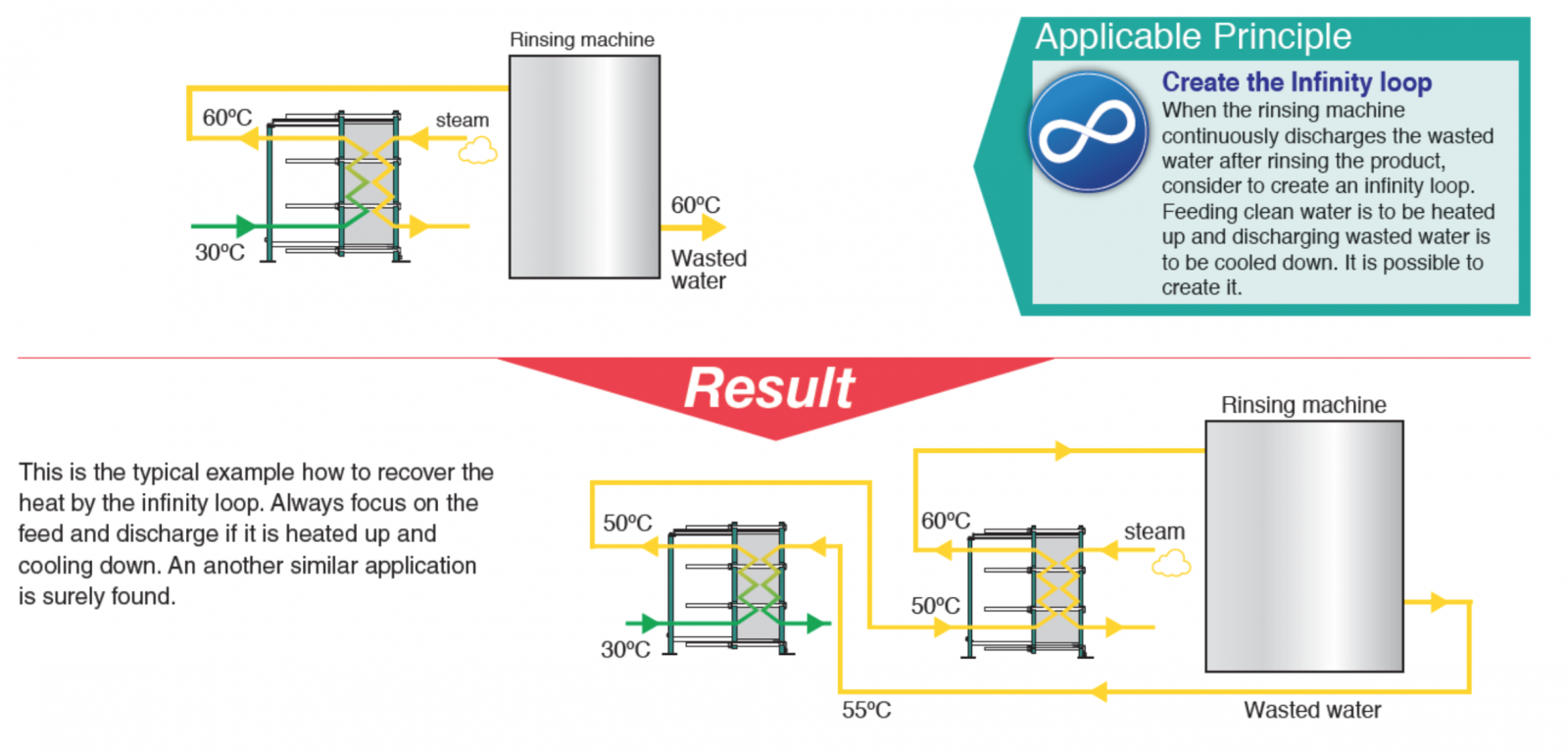
Energy recovery concept could be applied when a fluid requires heating and cooling in a series of process. For instance, a 30°C water need to be heat up to 60°C before reach to the rinsing machine and after completed process, the hot water was drain out as wasted water to treatment plant. To recover the energy, heat exchanger can be implemented as a preheater as shown in diagram below.

Economizer or Heat Recovery unit is an essential part of the process plant. Especially in South East Asia, Palm oil is produced majorly here. In Palm oil process plant, involves many steps. From the palm oil mill where Fresh Fruit Bunch is pressed and separated to get a Crude Palm Oil (CPO). The CPO will be then transferred to Refinery Plants where Removal of Scent and Colour happens. Final Product after removing impurities is called Refined Bleached Deodorized Palm Oil (RBDPO).
In Refining process, there is a lot of heating for the purpose of separation. There is a lot of cooling afterwards as finally it will be cooled for storage. Managing heat recovery is important. When heat recovery is optimized usage of steam can be reduced, saving utility cost.
The importance of an economizer is about the amount of heat it can recover. Temperature in Refinery can be up to 260°C in deodorization process. It is important that this heat can be utilized to substitute steam in other heating process.
Design of an economizer needs to be long heat transfer surface area to cool down high temperature to low temperature when it exits the economizer. Such example is the spiral heat exchanger, an equipment which heat transfer plates are rolled into a spiral channel for fluid to flow. Heat exchanges between hot and cold channel by the spiralling plates.
In heat exchange, thinner the plate is better for heat transfer. For spiral Heat exchanger, plate thickness is generally 1.0 to 2.0mm thickness. This is to ensure the bended plates are strong enough to withhold pressure in between two plates.
Of course, there are thinner plate heat exchanger, namely the gasketed type. However, gasketed type does not handle high temperatures. It is often used after the spiral heat exchanger where majority of the heat recovery takes place.
Some plant design will maximize their recovery by maximizing PHE heat recovery portion since the plate thickness is thinner. PHE maximum temperature is up to 180°C. Nevertheless, high temperature for PHE will cause breakdown much faster because of temperature and pressure. This causes plenty of problem for user maintenance team. It is best to select a durable and longer lasting equipment.
Another alternative for spiral heat exchanger is the fully welded heat exchanger which has plate thickness 1.0 to 2.0mm as well. Fully welded is gasket-less in between plates and can be cleaned by waterjet. It is more expensive in general compare to spiral type; however, the advantage is the heat transfer from plate corrugations, and maintainability. Being able to maintain helps as fouling occurs in certain period that also prohibits heat transfer.